BUILDING MANAGEMENT SYSTEM VÀ PROPERTY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
ARE THEY THE SAME?

Building Management System: Building management system
Property Management System: Property management system
Although their meanings may seem similar, are they really the same in terms of functionality?
Terminology:
-
BMS: Building Management System – Building management system
-
PMS: Property Management System – Property management system
-
POS: Point of Sales – Point of sale
-
HVAC: Heating, Ventilating, Air Conditioning – Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system
-
EMS: Energy Management System – Energy management system
-
Users: system users and customer experiencers
Basically, PMS is applied to tracking and managing documents and reports in building operations such as room booking, payment, guest data, online reservations, POS, and personnel management/organization.
BMS, also known as the building automation system, is applied to monitoring, supervising, evaluating, and reporting the status of technical building equipment such as temperature, electricity, ventilation, and more.
Common Features of BMS and PMS:
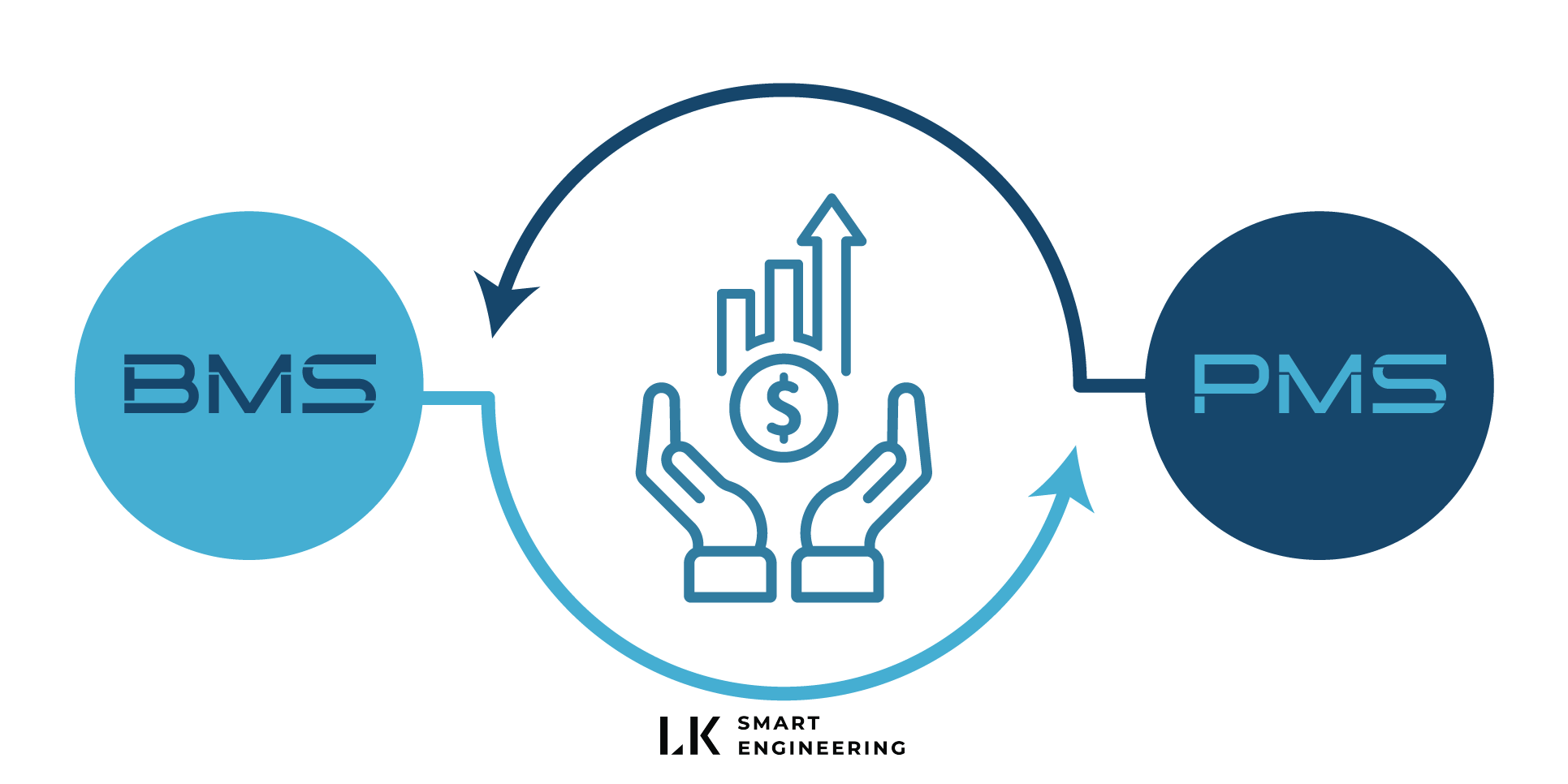
BMS and PMS are currently widely used in the hospitality industry, including restaurants and hotels. While PMS is used to manage front desk operations, bookings, and internal processes, BMS continuously monitors mechanical and electrical equipment in real time.
Therefore, operationally, the two systems are closely interconnected:
-
Streamlining and automating operational processes.
-
Continuous real-time management and monitoring.
-
Energy savings during operation → Cost savings.
How Are They Different:

Meaning:
Both systems involve management functions, but in reality, they represent two completely distinct aspects.
Energy consumption reporting: BMS or PMS?
In practice, BMS primarily controls the overall energy consumption of the building’s operation. The system enables managers and operators to monitor real-time energy usage and find ways to optimize it.
The trend is to apply Energy Management Systems (EMS) for more detailed (micro-level) support and management, maximizing operational energy efficiency.
PMS, however, cannot collect data related to EMS.
User Experience:
If BMS provides comfort in space and environment for users, PMS supports enhancing the user experience.
PMS offers users convenience and ease of service. Integration of operational management features in PMS helps meet user needs intuitively and instantly, such as entertainment/relaxation services or automated check-in/out convenience.
Moreover, PMS allows managers/operators to control or monitor systems with just a few simple actions.
Which system alerts first?
For example, when there is an HVAC issue, which system receives the alert?
-
BMS can predict and notify about potential risks before they occur. Operators/managers can schedule maintenance or repairs early, minimizing any negative impact on user experience. Thus, BMS acts proactively by forecasting problems and even estimating equipment lifespan.
-
PMS only detects when a device fails or loses signal. Most alerts come from users reporting issues to managers/operators, which negatively impacts the user experience directly.
Different Systems Becoming a Common Platform

Although BMS and PMS operate differently at the same time, applying both in building operations management—especially in hospitality—helps optimize operating costs effectively and maximally.
With the ability to integrate with extended, multi-functional systems, LK Smart Engineering has successfully combined BMS and PMS features into a specialized solution for digital transformation in businesses.
Optimize costs, elevate technology, and boost competitive advantage with the Smart Building solution from LK Smart Engineering.
( Nguồn: Sưu tầm)